"Outsourcing is the selection of suppliers with expertise in a particular area of business to produce and deliver a component part or service to another company" - Verma & Boyer, 2010.
“Outsourcing is the use of supply chain partners to provide products or services” – Bozarth & Handfield, 2012.
Over the past decade, outsourcing of noncore production and service activities to external suppliers has become a common method of streamlining and improving processes.
The use of outsourcing has increased for two primary reasons:
1. The total quality management movement in the 1980s helped increase companies' awareness that it is difficult to be "world class" in multiple activities and that settling for second-best products produced "in-house" just to maintain the work within a single organization is not the best approach.
2. The rapid increase in the in the capabilities of information technologies and other communication devices has made managing multitier supply chains much easier.
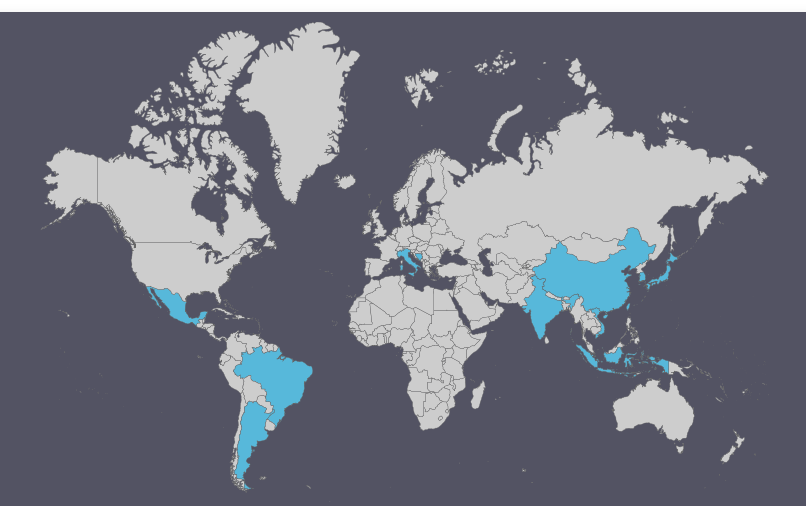
As one can
see in the chart above Nike kept its general positions such as Marketing,
Accounting, Promotion, General Management and Product Development in house.
http://han.hszuyd.nl/han/MarketlineAdvantage/advantage.marketline.com/Product?pid=8E563969-FC1C-4D3A-8EEE-F9D79F81F0C3
The 12 countries in blue indicate production places for Nike footwear,
which is being outsourced to low labour cost countries.
The countries are:
- Argentina
- Bosnia
- Brazil
- China
- India
- Indonesia
- Italy
- Japan
- Korea
- Mexico
- Taiwan
- Vietnam
Nike. Explanation of how it works in the
organisation and supply chain.
Nike
is not a production company and outsourcers almost all its shoes. Nike’s headquarters
is located in Beaverton, United States, which designs, develops and markets all
the footwear.
Subcontractors
are located in Taiwan and Korea and contract to other Asian countries for
production. Assembly factories that produce the footwear are located in Taiwan,
Korea, China, Indonesia and Vietnam.
The
manufacturing and assembly of their shoes is outsourced to third parties in
Asia. The manufacturers obtain the required raw materials by purchasing them
from suppliers.
Nike
made a conscious decision to retain the design and the marketing of the shoes
because Nike excels at product innovation and marketing of their shoes.
Companies should try to insource processes that are core competencies. These
are usually organizational strengths and abilities, which are developed over a
long period, that customers find valuable and competitors find difficult or
oven impossible to copy (C. Bozarth & B. Handfield, 2012)
After
the product is marketed the shoes will be sold to the customers by the Sporting
goods department and shoe stores, online, catalogue and other retailers, which
are not owned by Nike. The shoes will also be sold by Nike branded stores,
which are owned by Nike. Customers give feedback to Nike and this data will be
used in the development of the new products.
http://www.emeraldinsight.com/journals.htm?articleid=1733216&show=html
Production outsourcing
Advantages
One
of the main advantages that comes with outsourcing production to low labour
cost countries is the low-cost production. Because of this Nike can produce more
efficiently and reduce costs. As a positive consequence of this Nike can lower
the selling prices or increase their profit margins, which gives them a
competitive advantage over their competitors.
By
using an outsourcing strategy Nike has lower investment risk then by using an insourcing
strategy, because they do not have to invest in a production facility, so less
investment is needed up front. This gives them also more strategic flexibility
and access to state-of-the-art products and processes. The market or
technologies could change in the future. In this case it is often easier to
change supply chain partners than internal processes.
Disadvantages
A major disadvantage is
that there is always the possibility of choosing a bad supply chain partner.
The partner might not meet Nike’s expectations on capabilities or quality. If
badly produced shoes are being sold, it will have a bad effect on Nike’s brand
image. Outsourcing can also be bad for the brand image in the case the brand is
related to child labour and sweatshops. Furthermore, when outsourcing
production, Nike’s degree of control and coordination over processes and core
technologies could decrease.
If they would have
insourced their production, they could have increased their degree of control
and ability to oversee the entire production process. Next to that, the
business volume necessary to achieve economies of scale could be achieved more
easily. But a higher investment would be required and their strategic
flexibility could be reduced by this.
Conclusion
Nike outsources the production of the footwear in 12 countries worldwide. They made a conscious decision to retain the design and the marketing of the shoes because Nike excels at product innovation and marketing of their shoes. Even though they got lots of criticism about their outsource activities e.g. child labour in Asia and sweatshops, we think that Nike hugely benefits from its outsource strategy with reduced labour costs as main pinpoint.
Written by:
Ahmed Bairi, 1325157
Jan-Niklas Schmücker, 1325150
Kevin Doutzenberg, 1325152
Paul Erven, 1325142